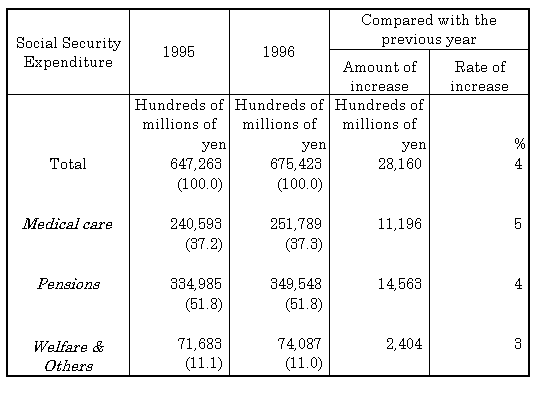
| (i) | Of the three categories, Medical care was estimated at 25,178.9 billion yen and its share of the total was 37.3 percent. Pensions was 34,954.8 billion yen and its share of the total was 51.8 percent. Welfare & Others was éV,408.7 billion yen and its share was 11.0 percent. |
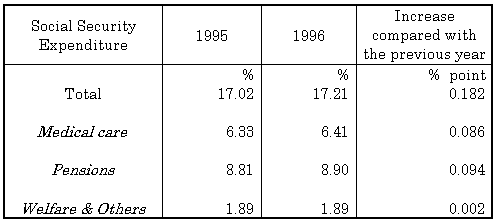
| (ii) | Social security expenditure increased by 4.4 percent fiscal year 1996. The percentage share of the National Income was 17.21 percent. |
| (iii) | Social security expenditure per head of population was estimated at 536,600 yen, and the average expenditure per household was 1,528,300 yen. |
| Table 1Social Security Expenditure by category, fiscal years 1995 and 1996 |
 |
| Note: ( ) Ratio to the total as a percentage. |
| Table 2Social Security Expenditure by category as percentage of National Income |
 |
| Table 3Social Security Expenditure per head of population and per household, fiscal years 1995 and 1996 |
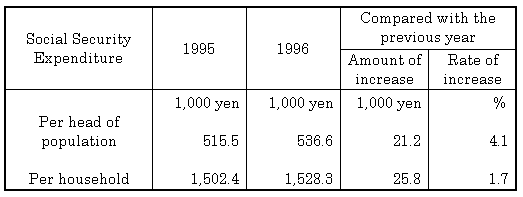 |
| Note: Social security expenditure per household = (Number of people in the household/Total number of households)ü~social security expenditure per head of population. |
| Figure 1 Social Security Expenditure by category, fiscal years 1970-1996 | 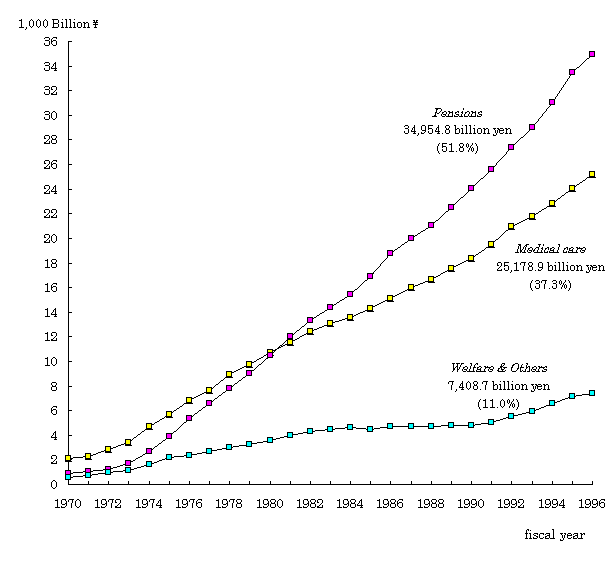
|
| Table 4Social Security Expenditure for the aged, fiscal years 1995 and 1996 |
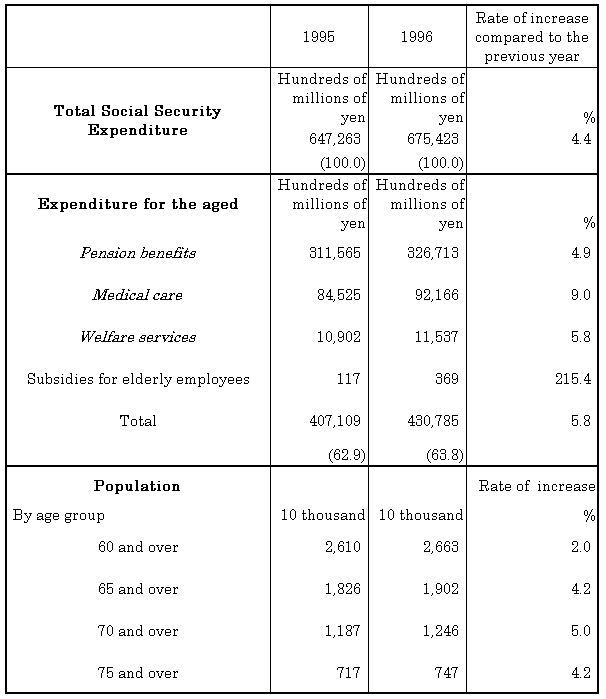 |
| Notes: |
| 1. ( ) Ratio to the total social security expenditure as a percentage. |
| 2. Medical care: Total expenditures of Health and Medical Services for the Aged excluding public health measures (e.g., medical check-ups and counseling, etc.). |
| 3. Welfare services: Government grants for nursing homes and home care for the aged (e.g., home-helpers, day-care services, respite care programs, etc.). |
| 4. Subsidies for elderly employees are grants in which, from the viewpoint of promoting continued employment and re-employment for 60 to 65-year-olds, 25 percent of the wages earned by people over 60 years old is provided to elderly people continuing to work whose wage has dropped considerably since turning 60. This grant is provided to elderly people under the age of 65. |